Jun 21st 2022
Why Solenoid Valves are Critical to the Automations and IoT Industry
Solenoid Valves - Applications:
Solenoid valves are becoming increasingly important in a variety of automated processes and are employed in a broad range of applications, such as automotive, aerospace, medical, food, and beverage. Following are a few applications, where Solenoid valves have become an irreplaceable choice of OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) in the industry:
- Automotive: fuel injectors, transmission shifters, turbochargers
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): automatic zone control, pneumatic thermostats, air conditioning, humidifiers
- Medical: oxygen concentrators, patient monitors, dialysis machines, oxygen concentrators
- Refrigeration: ice machines, water coolers, beverage dispensers
- Plumbing: Commercial dishwashers, water faucets, gas valves
Specific to the Automation and IoT industry, which is growing at a rapid pace, and expected to have a market size of $1.6 trillion by 2025, solenoid valves have gained prominence over the years and are used in a variety of applications such as:
- Connected devices: Condition monitoring to enable remote control and health monitoring of devices
- Smart homes: Fluid flow control in water purifiers, to control the flow of water, gas, and other media
- Industrial automation: Automated processes to improve efficiency and quality control
- Energy management: Temperature management to reduce energy consumption
Despite their applications and advantages, solenoid valves do have some disadvantages. For instance, they are not ideal for working with extremely viscous liquids since the plunger movement is restricted. They also have a limited lifespan owing to the fact that if the coil is energized for too long, it can overheat and burn out. Research and technological advancements in mitigating these challenges are underway.
As a result, it is critical to understand the functioning of solenoid valves and consider both direct and indirect factors before choosing the right type of solenoid valve for an application. This article is intended to offer essential information regarding the usage and selection of solenoid valves for industrial purposes, as well as in more particular terms for the automation sector.
About Solenoid Valves
A solenoid valve is an electro-mechanical device that, when energized, opens or closes a passage to control fluid flow. Their role can be to shut off, release, dose, distribute or mix fluids or gasses, all of which can pose a wide range of requirements and environments that must be accommodated in order to deliver reliable and effective service. The coil is the electrical component of the solenoid, and the valve body or pressure vessel is the mechanical component. When a solenoid (coil) is energized or de-energized, media passage through an orifice (or opening) is either stopped or allowed by the movement of a "core" that resides within the coil. The core is encased in a hermetic tube, making for a compact, watertight construction. Solenoid valves are often referred to with the term "electro-mechanical device" as they combine functions of electrical and mechanical components in a single unit.
Solenoid valves have many advantages over other conventional valve types. They are relatively simple and inexpensive to manufacture, and they can be controlled remotely, which makes them ideal for use in automated processes and hard-to-reach areas (such as underground oil pipelines). They can also be used to control the flow of very small amounts of fluid, making them ideal for use in laboratory and medical applications.
Solenoid Valve - Why it is Critical for the IoT and Automation industry:
Reason#1: Eliminates redundant process sensors
Built-in diagnostic sensors are now common in today's solenoid valves, including temperature, flow, and voltage monitoring. The information collected from these valves is utilized to control the valve via feedback and programmed loops, in comparison to merely displaying process values from standalone sensors. Such an SV configuration eliminates the need for additional temperature, flow, and voltage sensors while still allowing control of the process. Fluid power control is one of the primary uses for these systems.
Reason#2: Remote monitoring and control
Remote monitoring is essential for automated systems and Solenoid valves enable operators to manage the process lines and systems remotely even without direct access to the valve. The digital output data from an SV is hard-wired or transmitted over Cloud gateways, these actuators are controlled via mobile apps and programmed control panels. Hazardous applications such as radioactive and nuclear sites, and underground fluid supply lines typically use SVs over manual valves for this reason.
Reason#3: Automate Maintenance, Repair, and Troubleshooting
Repair and maintenance of damaged or failing equipment are detected in advance as the SVs communicate data directly from the process lines directly to the service company or OEM. This can prevent a problem from aggravating, and also eliminates the need for the technician to physically inspect the system in full beforehand. Technicians can also be notified that maintenance is required using IoT sensors' predictive maintenance methods. With the remote monitoring capabilities of an SV, the OEM and product owners can perform condition-based maintenance in real-time.
Reason#4: Ease of Re-programming and flexible operations
To optimize a production line or to adjust the flow parameters, it is critical for IoT and Automation engineers to select components that are flexible for re-programming. Solenoid valves meet this critical requirement, thanks to their variable flow and valve positioning/timing settings. Flow actuators need not be changed or replaced entirely with a change in requirement, as is the case with other valve actuators such as mechanical or pneumatic. Flexibility in re-programming not only saves the cost of modifying process lines but ensures machine up-time and production availability.
Reason#5: Connectivity and Universal Integration
The IoT and Industry 4.0 is fueled by the need for machines to "talk" to each other, and to the cloud. While Europe is familiar with protocols such as Profinet, EtherCAT, and Modbus RTU, North America uses Fieldbus such as DeviceNet, ControlNet, and Profibus. Therefore data sharing and integration between devices and control panels using different protocols is always a challenge. However, Solenoid valves with their digital output can be controlled by all major protocols, allowing for easy integration into existing systems as well as future-proofing for when protocols change or new control systems are developed.
Reason#6: Integrated Power Supply and Energy Efficient Actuation
The 24 VDC power supply is standard for all industrial automation equipment (IoT Gateways, data loggers, indicators, annunciator panels, etc.) and for most solenoid valves, which makes it easier to find a compatible universal power source, also reducing the cost of labor and wiring. The low coil power consumption of today's actuators also contributes to a reduction in heat generation, making them ideal for use in close (tight) spaces. Whereas traditional actuators require 100 - 120 VAC power, which may be a safety hazard in environments such as oil rigs and underground pipelines.
Benefits of using Solenoid valves for automation and IoT industry:
- Solenoid valves can be operated remotely, allowing for remote fluid control and integration with Cloud for data analytics, condition monitoring, and remote operations. These valves may be programmed to open and close at specific intervals or when a particular (condition or) event occurs, making them ideal in automated systems.
- Solenoid valves can be controlled with a variety of input signals, such as digital (on/off), analog (0-10 VDC or 4-20 mA), and pneumatic (air pressure). This allows for easy integration with different types of control systems.
- Solenoid valves can be configured in a variety of ways, such as normally open (NO), normally closed (NC), and universal (UN). This allows for more flexibility in the system design.
- The response time of the solenoid valve is in milliseconds (ms). This is much faster than the human reaction time, making them ideal for use in applications where fast response times are required, such as in automotive and aerospace applications.
- Solenoid valves require less power to operate than other types of valves, making them more energy-efficient. They are also available in a variety of voltages and can be powered by batteries, making them ideal for use in portable applications.
- Solenoid valves are more reliable than manual valves and when properly maintained have a longer lifespan. Due to their reliability, they are often used in mission-critical applications.
- Solenoid valves are available in a variety of sizes and shapes. They can be used for both low-pressure and high-pressure applications such as in medical, automotive, and aerospace applications.
- Solenoid valves are available with a variety of actuator types, such as spring return, double-acting, and fail-safe. This allows for more precise control of the fluid flow.
Case studies - Solenoid Valves applied for Automation and IoT:
Following are a few success stories demonstrating the effective application of solenoid valves in conjunction with automation and IoT:
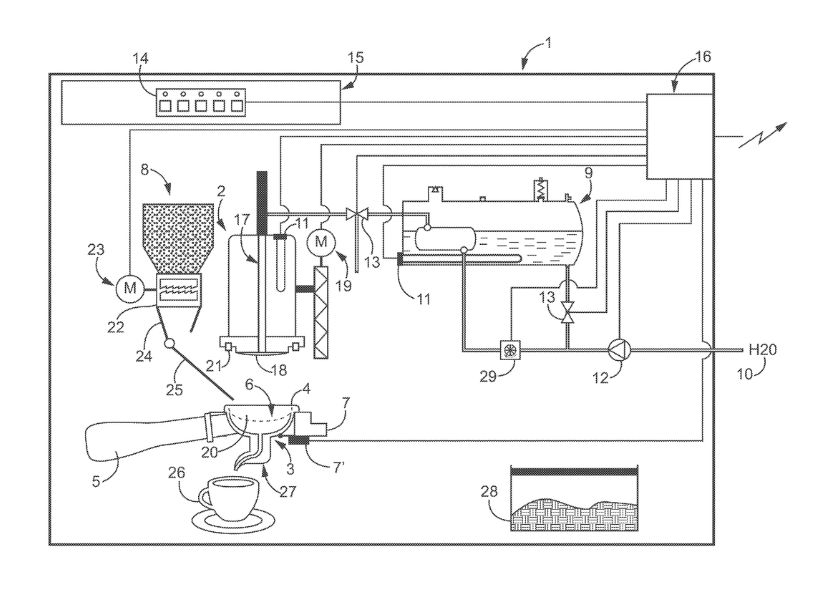
- Fully Automatic Coffee Machines: Several high end coffee machine manufacturers have created “super-automatic coffee makers” which utilize multiple solenoid valves for various processes to serve various coffee recipes to its users. The solenoid valves were used to mix coffee, steam, water, and hot water and to separate the non-media from the end product. These valves are programmed to operate as per the customer’s selection of choice and preferences, and pre-set to actuate at low power and high-temperature modes. The valves are designed to coordinate and allow the flow of steam and hot water mixtures and provide instant coffee. Due to an optimized design, the maintenance time for replacing the coil, diaphragm, and opening the fluidics to replace the plunger or the seal has significantly reduced. This fully automated machine is tested and approved by the US regulatory bodies for commercial use.
- Anti-lock brake system (ABS): ABS is a classic example of the automation capabilities of solenoid valves. When the driver presses the brake pedal, the pressure sensor senses the pressure and sends a signal to the electronic control unit (ECU), which activates the solenoid valves. The solenoid valves open and allow pressurized brake fluid to flow into the brake calipers to apply pressure to the brake pads, which in turn press against the brake rotors. This process slows down the wheels and prevents them from locking up. When the solenoid valves are deactivated, the pressurized brake fluid is released and the calipers return to their original position. This life-saving system prevents the wheels from locking up and skidding, which could lead to loss of control of the vehicle.
- An Innovative Internet of Things (IoT) Based Smart Electric Valve Monitoring and Controlling System research presents a Solenoid Valve - IoT-based technique to control any fluid's flow. The study demonstrates preventing the wastage of water and other process fluids by timely reporting the unnecessary water flow and Real-time Monitoring of Fluid Flow through push notifications about the flow and Valve positions (On/off), on any smart appliance (phone, tablet, or PC).
- Research in Thailand has successfully implemented a Solenoid Valve-based IoT solution for Semi-Automated Mushroom Cultivation House to reduce the manual workforce and work hours. Now farmers can monitor and control the temperature, humidity, and solenoid valve status of mushroom houses from the smartphone application.
Solenoid valves - Current State of Innovation:
Before the invention of solenoid valves in the early 19th century, the only way to control the fluid flow was by using manual valves. This meant that the operator had to be physically present to regulate the valve. With the advancements in electrical technology, electronic actuators were invented, leading to the development of solenoid valves. The first solenoid valves were large and bulky and could only be used for low-pressure applications. Over the years, solenoid valves have been miniaturized and are now available in a variety of direct and pilot operating types, capable of operating in high-pressure applications, such as dams and hydropower stations.
The early solenoid valves were also prone to coil burnout and clogging of plungers due to fluid intrusion within the magnetic coils. Thanks to advances in materials and manufacturing processes, today's solenoid valves have tight seals to compartmentalize fluids at higher pressures. Simulation and FEA (Finite Element Analysis) studies have ensured the reliability of SVs to function even under extreme environmental conditions.The third major advancement in solenoid valves is the evolution of low power-consumption models. Since the 1990s, OEMs have given considerable focus on energy optimization, leading to the development of sub-5-watt Solenoid valves, which resulted in significant energy savings for the process industries worldwide.
Today solenoid valves have become more reliable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective, and are also expected to have a longer lifespan and with custom configurations, adding ease of integration to the IoT and Automation sector. Following are some notable technological advancements in solenoid valves newly available and/or expected in the coming years:
- Double coil technology: The introduction of direct-acting double coil technology has resulted in significant energy savings. This uses two separate windings, one for high power and the other for low power. The high power coil opens the valve, and integrated electronics switch to the low power winding to provide the holding force and maintain the valve in its position. This twin coil approach is powerful enough to open the valve but uses 75 percent less electricity to hold the valve in its position.
- Energy-saving Coil designs: Optimizing the coil operation and its design is seen to have a direct impact on the energy savings and valve performance. Unlike the double coil solenoid valves, which with high and low power windings, even in single-coil conventional valves, energy-saving designs have resulted in a significant reduction in power consumption. These valves have integrated wiring which initially causes the coil to be overly excited to open or close the valve (depending on the NO/NC type), and in a fraction of a second, the excitation current is reduced by 95 percent, which is sufficient to hold the valve in its position. Process industries adopting this feature can have tremendous energy cost savings over time.
- Next-Gen Low Power SVs: With the newest generation of truly low-power solenoid valves rated at 0.5 to 0.75 watts, designs are approaching the magic half-watt mark. These lower-powered components are altering the rules of the energy consumption game among different actuator types, with predictions suggesting millions of dollars in savings in energy usage. The installation costs of Solenoid valves that are designed around the emerging half-watt standard can be reduced with Bus bars rather than Traditional point-to-point wiring methods, which often result in higher installation costs (labor, cables, and conduits, fittings, connectors, I/O, and plant real estate). These valves also eliminate the need for extra power isolation relays, allowing smaller and less expensive wiring gauges to be used.
Research studies aimed at predicting failures and improving the reliability of solenoid valves:
- Predicting the useful life of Solenoid valves: Maintenance decisions may be made ahead of time if the remaining useful life (RUL) of Solenoid Valves (SVs) can be accurately predicted. Although identifying an SV's RUL is difficult due to its advanced architecture, multi-physics coupled operation mechanism, and complicated degradation processes, researchers have successfully utilized and validated data-driven predictive methods based on data-driven exponential models.
- Early Detection of Coil Failure: Fault-induced changes in the coil resistance are isolated from thermal influences and offered as a cost-effective solution that requires no special equipment. For realistic fault sizes, the technique was found to be able to detect early indications of coil failure and produce robust performance and high detection rates.
- Failure Mechanism Study of Solenoid Valves: Based on Thermal-Structure Finite Element methods, solenoid valve models are constructed to provide useful information such as temperature distribution and stress distribution for failure mechanism study. Results predict that the failure of the solenoid valve is closely related to the thermal expansion inside the coil. These studies provide a reference for failure mechanisms and assist future researchers in enhancing the efficiency and in prolonging the life of solenoid valves.
Summary:
Solenoid valves are critical components in the IoT and Automation industry due to their wide range of applications and benefits. When selecting a solenoid valve, it is important to consider the specific needs of your application and to check for compliance with regional standards. The future of solenoid valves looks promising, with new advances to improve their service life, efficiency, and performance, adding immense value to the Automation sector.
At Electronic Solenoid Valve, we prioritize Automation and offer industry-leading Solenoid valves specific to your application. Our range of solenoid valves are available with a variety of configurations, sizes, safety standards, and actuation types and can be custom-integrated, so you can find the perfect valve for your requirements.
To view our full range of solenoid valves -


