Posted by Electric Solenoid Valves on Sep 8th 2025
Avoid Leaks: Match NPT Thread Size & Port for Solenoid Valves
Choosing the wrong port or thread is one of the fastest ways to end up with leaks, returns, and downtime. This quick guide gives you a practical NPT thread size chart up front, then walks you through how to measure outside diameter (OD), confirm thread pitch (TPI), and avoid mixing standards like NPT vs BSP. You’ll also get Cv-based pointers so you can select a solenoid valve that fits and flows the way your system needs.
Whether you’re speccing an OEM build, replacing a field fitting, or troubleshooting a weeping connection, use this guide to verify the thread, match the port, and move on with confidence
Quick NPT Thread Size Chart
Match the measured male thread OD to the nominal NPT port size. Tip: use a caliper and measure across the first full thread on a male fitting.
|
NPT Size |
Threads per Inch (TPI) |
Male Thread OD (in) |
Male Thread OD (mm) |
Typical Cv Range (indicative) |
|
1/8" |
27.0 |
0.405 |
10.29 |
0.2 – 0.6 |
|
1/4" |
18.0 |
0.54 |
13.72 |
0.6 – 1.5 |
|
3/8" |
18.0 |
0.675 |
17.14 |
1.5 – 2.8 |
|
1/2" |
14.0 |
0.84 |
21.34 |
3 – 7 |
|
3/4" |
14.0 |
1.05 |
26.67 |
7 – 12 |
|
1" |
11.5 |
1.315 |
33.4 |
10 – 18 |
|
1-1/4" |
11.5 |
1.66 |
42.16 |
18 – 35 |
|
1-1/2" |
11.5 |
1.9 |
48.26 |
35 – 55 |
|
2" |
11.5 |
2.375 |
60.32 |
55 – 100 |
*Cv ranges are indicative and vary by valve design and/or orifice. Measure OD at the first full thread. NPT uses a 60° tapered profile.
How to Measure NPT Threads (OD & Pitch)
- Identify male vs. female. Male threads are external (measure OD). Female threads are internal—confirm with a known male or plug gauge.
- Measure OD on male NPT. Place calipers across the first full thread (not the tapered lead). Compare to the chart to find nominal size—for example, ~0.840" ≈ 1/2" NPT.
- Confirm pitch (TPI). 1/2" & 3/4" NPT are typically 14 TPI; 1/8" is 27 TPI; sizes ≥1" commonly use 11.5 TPI.
- Remember the taper. OD varies along the thread. Measure from the same reference point each time.
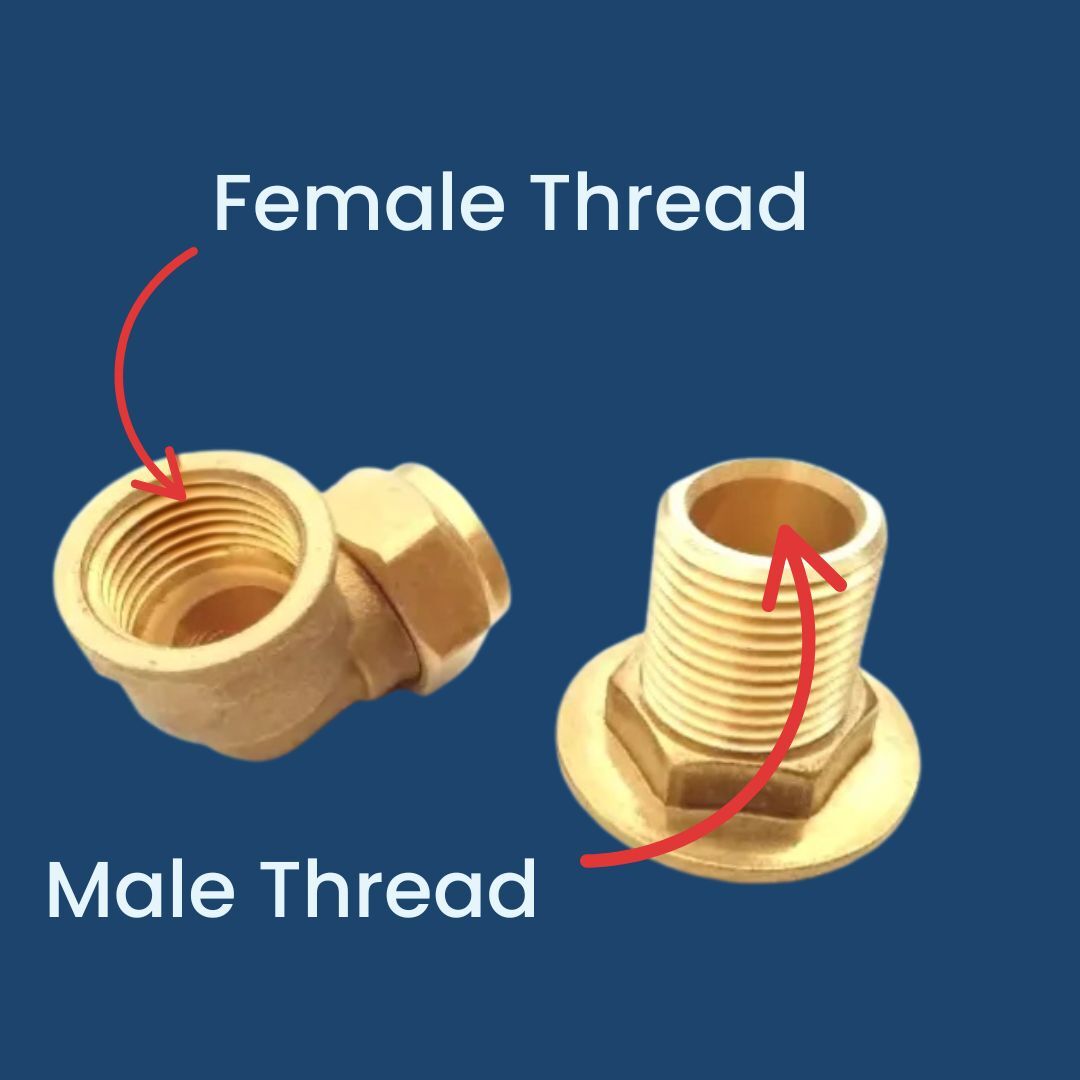
Common mistakes: measuring the lead thread, assuming nominal size equals OD, or mixing NPT and BSP standards.
NPT vs. BSP: What’s the Difference?
Cross‑threading or weeping often comes from a thread standard mismatch.
- NPT (National Pipe Taper): tapered, 60° thread angle; seals by thread interference; commonly installed with PTFE tape or compatible pipe dope.
- BSP: BSPP (G) is parallel and typically seals with a washer or O‑ring; BSPT (R) is tapered but uses a 55° angle. Pitch/OD often differ from NPT.
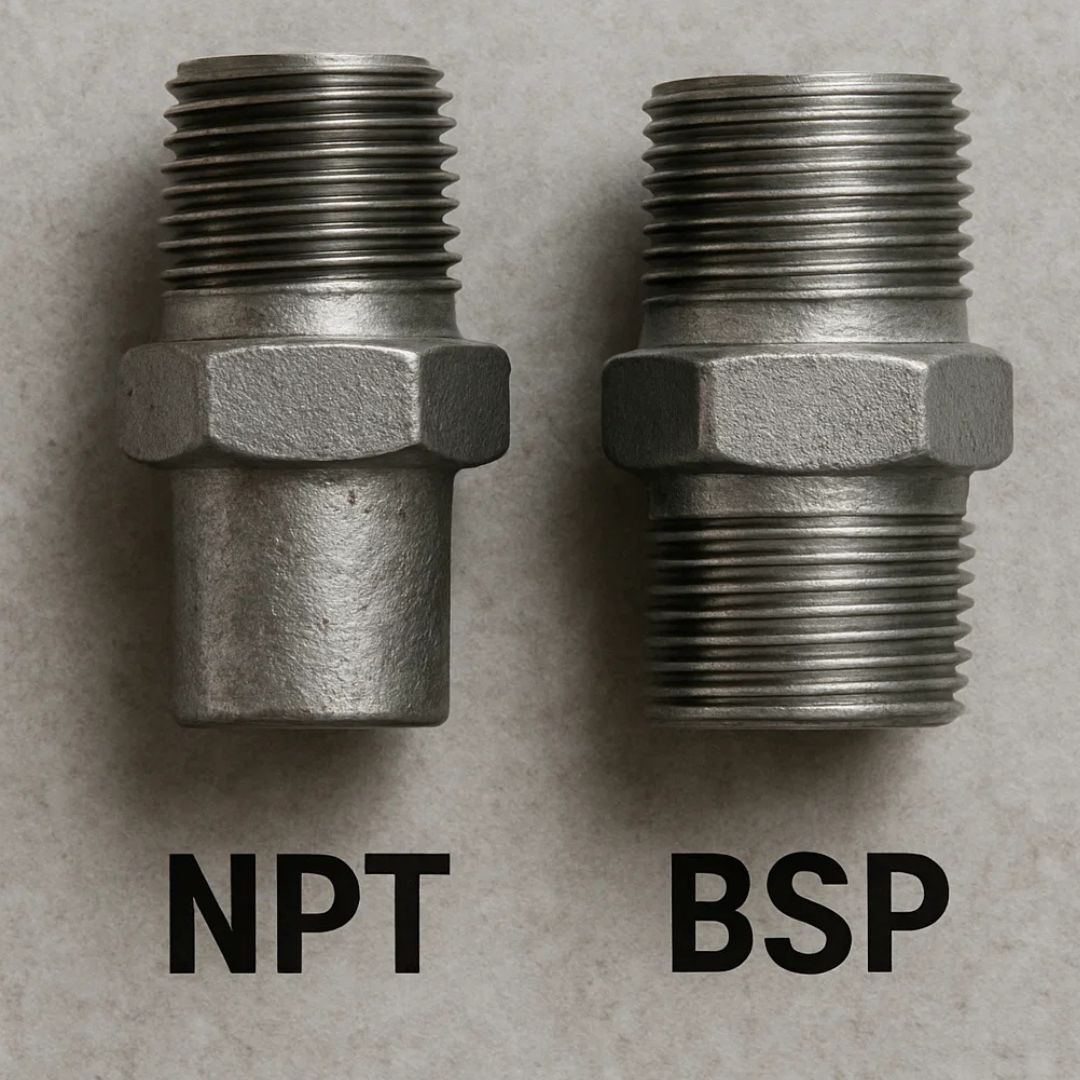
Bottom line: Do not mix BSP with NPT unless you’re using an adapter rated by the manufacturer.
Port Selector: Match Your Valve, Cv & Port
Choose ports by both fit and flow. Start with Cv, then confirm the NPT size.
- 1/8" NPT (Cv ~0.2–0.6): pilot circuits, instrumentation air, small orifices.
- 1/4" NPT (Cv ~0.6–1.5): general‑purpose low/medium flow, compact manifolds.
- 3/8" NPT (Cv ~1.5–2.8): higher flow pneumatics, light liquids.
- 1/2" NPT (Cv ~3–7): common for water, air, inert gas at mid‑flow.
- 3/4" & 1" NPT (Cv ~7–18): high‑flow circuits and larger orifices.
- 1‑1/4" to 2" NPT (Cv ~18–100): bulk transfer, rapid fill/vent.
Sizing by Cv is more reliable than port size alone. For viscous media or low ΔP, consider larger ports or zero‑differential valves.
Installation & Sealant Tips (Leak‑Free Checklist)
- Use the right sealant: 2–3 wraps of PTFE tape (clockwise) or a compatible pipe sealant—avoid over‑taping.
- Don’t over‑torque: tapered threads can crack bodies or distort seats. Tighten to spec, then test.
- Support the body: use a backup wrench to avoid twisting the valve during installation.
- Flush the line: debris can damage seats and cause weeping.
- Final test: pressurize and leak‑check with soapy water or an approved method.
Correctly identifying NPT thread size comes down to three steps: measure the male thread OD at the first full thread, confirm the thread pitch (TPI), and make sure you’re using the right standard (NPT vs. BSP).
Once your port is confirmed, choose the solenoid valve by required flow (Cv), media, and pressure. Follow the sealant and installation checklist to avoid weeping, galling, and costly do-overs—then leak-check to validate the connection.
FAQs
Why doesn’t my measured OD match the nominal pipe size?
NPT uses nominal sizes from pipe standards. The measured OD corresponds to the thread profile, not the stated size. Use the chart to match OD → nominal.
Can I thread NPT into BSP?
No. Differences in angle (60° vs 55°), profile, and pitch can cause damage and leaks. Use the correct standard or a rated adapter.
What if my TPI matches, but it still leaks?
Matching TPI isn’t enough—verify thread angle and tapered vs. parallel form. Also, check the sealant and torque.
Do I need thread sealant with NPT?
Yes. NPT seals by thread interference, so PTFE tape or a compatible pipe dope is typically required.

