Apr 22nd 2024
Precision Flow Management: Understanding How 3-Way Solenoid Valves Work
A 3-way solenoid valveis a vital component in many industrial and residential systems, offering greater control and versatility over the flow of fluids or gasses compared to its 2-way counterpart. These valves are designed to direct the flow of media through three distinct ports, enabling precise regulation of pressure, flow rates, and system functionality. Understanding the working principles of a 3-way solenoid valve is crucial for efficient system operation and maintenance.
What is a Solenoid Valve
Starting with the basics, let’s quickly go over what a solenoid valve is.
Solenoid Valves are electromechanically operated valves. The main parts of a SV are the valve body, solenoid coil, and plunger. When the coil is energized, the plunger moves to control the flow of media.
2 Way Solenoid Valves
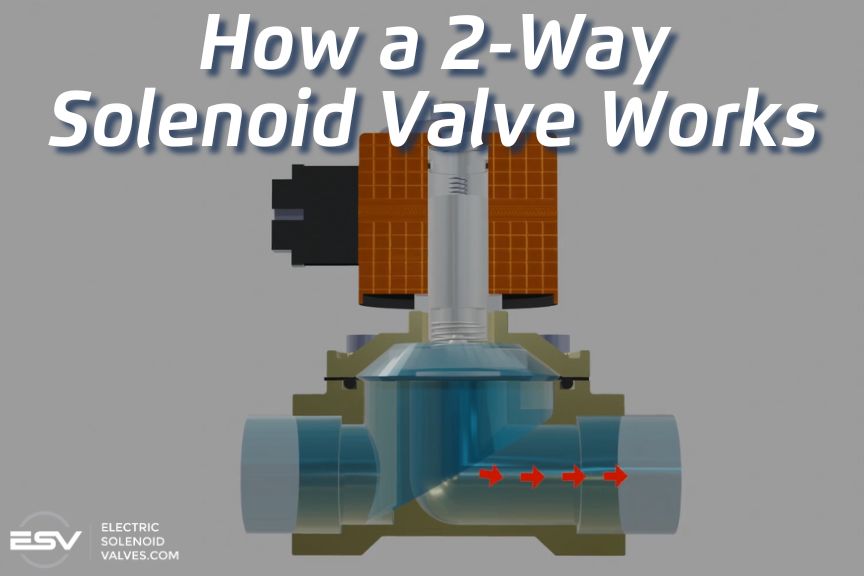
2 way solenoid valves are the most common types used.
These valves have two ports, one for the inlet and one for the outlet. When the valve is energized, the plunger moves either up or down (depending on the type of solenoid valve), opening or closing the flow of media through the valve.. When the valve is de-energized, the plunger moves to its starting position, starting or stopping the flow of fluid (depending on the type of solenoid valve).
Read more - How a 2-Way Solenoid Valve Works - Electricsolenoidvalves.com
What is a 3 Way Solenoid Valve?
![A 3-way solenoid valve with three ports labeled: inlet port (body orifice port), outlet port (cavity port), and exhaust port (stop port). The valve also has a solenoid coil wrapped around the body. Text within the image identifies the main parts of a 3-way solenoid valve including the valve body, plunger, and solenoid coil. [/Image description] A 3-way solenoid valve with three ports labeled: inlet port (body orifice port), outlet port (cavity port), and exhaust port (stop port). The valve also has a solenoid coil wrapped around the body. Text within the image identifies the main parts of a 3-way solenoid valve including the valve body, plunger, and solenoid coil. [/Image description]](/product_images/uploaded_images/3-way-solenoid-valve-ports.jpg) A 3-way solenoid valve, on the other hand, has three ports: an inlet, an outlet, and an exhaust. Unlike 2-way valves, 3-way solenoid valves let you control the flow of fluid or gas in three different directions for much greater control over the flow of fluids.
A 3-way solenoid valve, on the other hand, has three ports: an inlet, an outlet, and an exhaust. Unlike 2-way valves, 3-way solenoid valves let you control the flow of fluid or gas in three different directions for much greater control over the flow of fluids.
3 Ports
Inlet (Body Orifice Port):
- This is where the fluid or gas enters the valve.
Outlet (Cavity Port):
- Where the fluid or gas exits the valve after being directed by the valve's internal mechanism.
Exhaust (Stop Port):
- Allows the release of pressure or fluid when the valve changes position.
2 Orifices
Within the valve, there are two orifices, each of which is used to control the flow of fluid or gas passing through it. At any given time, one orifice will be blocked by the plunger and one will be open.
Exhaust (Stop Orifice):
- Located in the exhaust port
- When the valve switches positions, it opens or closes the exhaust port, managing pressure differentials within the system
Inlet/Main (Body Orifice):
- Located in the inlet port
- Needs to be energized for media to flow into this port.
The size and shape of the orifices determine the flow rate and pressure drop across the valve.
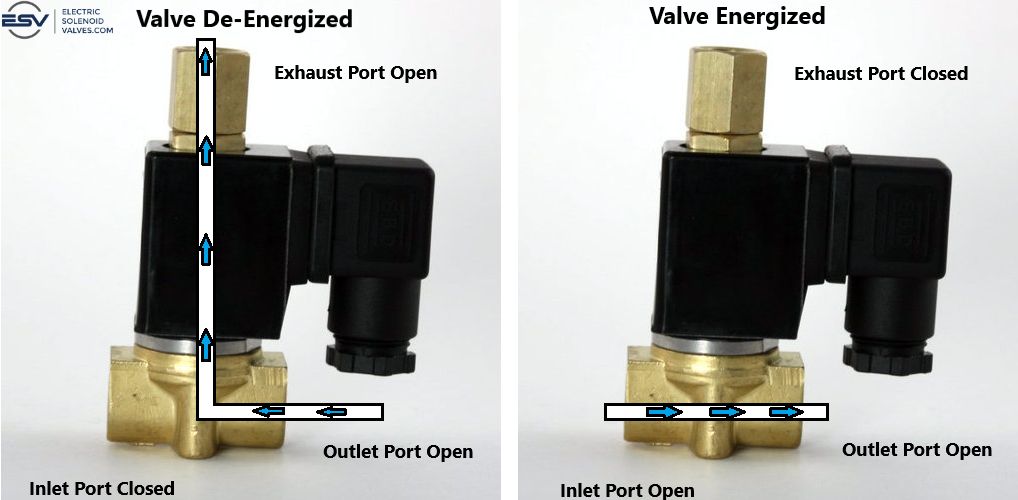
Energizing and De-Energizing the Valve
Energizing and de-energizing the valve controls the flow direction of media in the system. In a normally closed valve (the most common type), the plunger remains in the closed position when de-energized, and requires energy to open it. Energizing (turning on) the valve lifts the plunger, changing the flow path.
- Energized: When the valve is open (energized), the plunger opens the inlet orifice and closes the exhaust orifice. The fluid or gas flows through the inlet orifice and into the outlet port, while the exhaust port is blocked off.
- De-energized: When the valve is closed (de-energized), the inlet orifice is blocked, preventing flow from entering that port. The liquid or gas in the system now flows from the outlet port to the, now open, exhaust port.
Significance of the Exhaust Port
The exhaust port, despite its seemingly simple design, plays a critical role in the operation of a 3-way solenoid valve, providing a relief pathway for the media. This feature is particularly significant in systems where pressure buildup or fluid accumulation could lead to potential hazards or inefficiencies.
What are the benefits of the exhaust port?
The exhaust port provides pressure relief, enhances the valve performance and system safety, minimizes response time, saves energy, reduces maintenance and downtime, and complies with some safety standards.
- Pressure Relief:
- The exhaust port provides controlled pressure release from the valve chamber when the valve is off, preventing pressure buildup and maintaining valve integrity and system safety.
- System Safety:
- The exhaust port improves system safety by preventing sudden pressure or flow changes, minimizing the risk of water hammer and damage to components.
- Valve Performance Enhancement:
- The exhaust port facilitates rapid pressure release during valve switching, reducing response time and enhancing system responsiveness.
- Energy Efficiency:
- The exhaust port reduces energy needed to overcome backpressure, leading to better efficiency and lower operational costs.
- Reduced Maintenance and Downtime:
- The exhaust port extends component lifespan, by preventing component wear and tear and mitigating damage caused by pressure spikes or fluid accumulation. This benefit can aid in saving costs and boosting productivity
- Compliance with Safety Standards:
- The exhaust port ensures safe venting and capture, creating a safe environment and meeting safety standards.
Common Applications of 3-Way Solenoid Valves:
3-way solenoid valves have a breadth of applications across various industries. Some common applications include:
Coffee Shops & Espresso Machines
- Releasing 'Spent' Pressure: After extracting espresso, the puck of coffee grounds is highly pressurized. The exhaust quickly dissipates this pressure, allowing a barista to remove the portafilter immediately and safely transition to preparing the next espresso shot.
- Drying the Puck: The release of pressure also helps dry out the coffee puck slightly, making it easier to cleanly knock out of the portafilter.
- Preventing Backflow: When the machine is not brewing, the exhaust port prevents any residual water or steam pressure from flowing back up into the brew group, which could affect the next shot's consistency.
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems
- Refrigerant Flow Control: 3-way SVs can direct the flow of refrigerants in air conditioning systems, enabling efficient cooling and heating cycles.
- Air Handling: These valves can control the flow of air in ventilation systems, optimizing proper air circulation and filtration.
- Water Management: They can also regulate the flow of water in heating and cooling systems to efficiently transfer heat and conserve energy.
Automotive Industry
- Fuel Injection: They regulate the flow of fuel in fuel injection systems, and protect against backflow.
- Emission Control: These valves play a role in controlling the flow of exhaust gasses in emission control systems.
- Climate Control: They can direct the flow of refrigerants in automotive air conditioning systems.
Water Treatment and Distribution
- Treatment Processes: 3-way solenoid valves can regulate the flow of water, chemicals, and other media during various water treatment processes, such as filtration, disinfection, and desalination.
- Irrigation and Sprinkler Systems: They can control the flow of water in irrigation and sprinkler systems.
- Backflow Prevention: The exhaust port helps prevent the backflow of contaminants into the water supply, protecting the system's integrity and public health.
Pneumatic Systems and Automation
- Actuator Control: 3-way solenoid valves can direct the flow of compressed air to pneumatic actuators, enabling precise motion control and automation.
- Tool Operation: They can regulate the flow of air in pneumatic tools, such as impact wrenches, drills, and grinders to operate efficiently and safely.
- Vacuum Systems: The exhaust port can be used to vent or release air in vacuum systems, enabling precise control and preventing potential damage from excessive pressure.
Explore Our 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Are you searching for high-quality 3-way solenoid valves? We have them in stock and ready to ship within one business day. If you have any questions or need assistance, don't hesitate to contact our valve experts by phone, email, or online chat. We're here to assist you.