Jun 24th 2024
How to Automate and Remotely Control Valves at Home
I remember when I was a kid one of my favorite parts of Disney World was the Carousel of Progress. The fourth act of it showed a ‘futuristic’ world where everything was automated which included a funny interaction with voice activation gone horribly wrong. I always thought that stage was pure science fiction we would never get to see. Well most of it has come true and with most of the kinks worked out.
Automation is now something we all see in our everyday lives. Today we can control our lights thermostats and even our coffee makers automatically or with a simple voice command. One aspect of home automation that has become increasingly popular and practical is the ability to control valves remotely. One area where this automation is making a huge difference is in the control of valves.
Valve automation is the process of controlling valves automatically or remotely to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. This technology once only available in industrial settings is now making its way into our homes offering convenience efficiency and peace of mind.
This guide will cover all the ways you can set up electric control valves as well as how to set them up for various applications. We will break it down into different types of automation integration techniques as follow:
- Simple Automation Solutions: Basic plug-in timers and smart plugs/switches.
- Smart Home Integration: Smart home hubs and voice control
- Advanced Automation Solutions: DIY Microcontroller Projects and Sensor-Based Automation
Jump Ahead
- Why Automate Valves at Home?
- Valve Automation Basics
- Simple Valve Automation Solutions
- Smart Home Integration
- Advanced Valve Automation
- Choosing the Right Solution
- DIY Valve Automation Projects at Home
Why Automate Valves at Home?
There are many benefits to setting up valve automations at home. Just a few of them are:
- Convenience: Control your valves from anywhere using your smartphone or voice commands. No more running to the basement to adjust the water heater or rushing home to turn off the sprinklers.
- Efficiency: Automated valves can optimize water usage saving you money on your utility bills and reducing your environmental footprint.
- Safety: Prevent water damage by automatically shutting off valves in case of leaks or overflows.
- Comfort: Maintain a consistent temperature in your home by automating your heating and cooling systems.
- Smart Home Integration: Seamlessly integrate valve automation into your existing smart home ecosystem for a truly connected living experience.
Whether you're a tech-savvy homeowner looking to create a fully automated smart home or just want to make parts of your daily routines a little easier valve automation has something to offer everyone.
Valve Automation Basics
Before getting into different automation solutions it’s a good idea to understand some of the fundamentals of valve automation systems.
Types of Valves for Automation
Several types of valves can be automated each with its own benefits:
- Electric Ball Valves: Offer quick shutoff and full flow when open.
- Solenoid Valves: Electrically operated valves ideal for remote control.
- Butterfly Valves: Provide good regulation in larger pipe diameters.
- Globe Valves: Excellent for regulating flow and frequent operation.
The best valve you should use depends on the application required flow rate and the medium being controlled (water gas etc.).
Basic Components of an Automated Valve System
An automated valve system typically consists of three main components:
- Valve: The actual device you’re trying to automate. This mechanical device controls the flow of liquid or gas.
- Controller: This is the brains of the system that sends a signal to the valve to open and close.
- Power Source: Supplies the necessary energy which could be a standard electrical outlet batteries or even solar panels.
- Communication Module: For remote control often using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
Overview of Control Methods
Valve automation systems can be controlled by:
- Timers: Simple scheduling for regular operations.
- Sensors: Respond to environmental conditions like moisture or temperature.
- Remote control: Operate valves via smartphone apps or web interfaces.
- Voice commands: Integration with voice assistants for hands-free control.
- Programmable logic: Advanced control based on multiple inputs and conditions.
Simple Valve Automation Solutions
Let's start with the simplest and most affordable ways to automate your valves. These techniques are perfect for beginners and those who want to test out home automation without breaking the bank.
Basic Plug-in Timer

A plug-in timer is a fairly simple device that you plug into a standard electrical outlet. You can set it to specific times to turn your valve on and off.
Common and practical uses
- Automated watering for gardens or lawns
- Timed filling of pools or water features
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Easy to install inexpensive no internet connection required reliable.
Cons: Limited functionality no remote control not be suitable for complex automation
Basic Setup Instructions
- Plug the timer into a standard electrical outlet.
- Plug your valve into the timer.
- Set the desired on/off times on the timer.
- Test the valve to ensure it's working correctly.
Smart Plugs and Switches

Smart plugs and switches are similar to basic timers but they offer additional features like remote control and smart home integration. They are connected to either Wi-Fi or Bluetooth making it easy to control by a smartphone or computer. Smart plugs and switches can be controlled remotely from an app by voice commands with a smart home assistant or set up on a schedule.
Common and Practical Uses
- Remote control of irrigation systems for lawns or gardens
- Automatically filling pet water bowls
- Scheduled activation of water features or fountains
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Remote control easy to set up with smart home systems more flexible scheduling options versatile.
Cons: Requires Wi-Fi more expensive than basic timers may require some technical setup.
Basic Setup Instructions
- Plug the smart plug or switch into a standard electrical outlet.
- Plug your valve into the smart plug or switch.
- Download the manufacturer's app and follow the instructions to connect the device to your Wi-Fi network.
- Use the app or voice commands to remotely control the valve or set up automations.
Smart Home Integration
Smart home integration takes valve automation to the next level allowing you to control your valves seamlessly along with other smart devices in your home.
Smart Home Hubs

At the center of a smart home ecosystem you’ll find a smart home hub. These are devices like Amazon Echo or Apple HomePod that act as a central command center to control various smart devices around your home. They use various wireless protocols like Wi-Fi Zigbee and Z-Wave to communicate with your smart devices. You can then use the hub's app or voice commands to control your valves along with other devices like lights thermostats and security cameras.
Common and practical uses
- Coordinating valve control with other smart home devices (e.g. turning off sprinklers when smart weather stations detect rain)
- Centralizing control of all smart valves in one interface
- Controlling smart plugs and switches giving you all of the uses mentioned in the section above
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Centralized control of all smart devices integration with various devices from different manufacturers enhances home automation with advanced automation possibilities. voice control and remote access often provides a more user-friendly interface.
Cons: Initial setup can be complex requires compatible devices can be expensive to set up requires a Wi-Fi connection may some technical knowledge to set up and configure.
Examples of Smart Home Hubs
- Amazon Echo
- Google Nest Hub
- Apple HomePod mini
- Samsung SmartThings Hub
- Apple HomePod
Basic Setup Instructions
- Choose a hub compatible with your existing smart devices.
- Set up the hub according to manufacturer instructions.
- Add your smart valves or device controlling your valves to the hub's network.
- Create automations or scenes involving your valves.
- Control your valves through the hub's app or interface.
Voice-Controlled Valves

Valves can be controlled with voice control operations when connected to smart home assistants like Amazon Alexa Google Assistant or Apple's Siri. This allows you to control your valves using voice commands adding an extra layer of convenience to your smart home setup.
Common and practical uses
- Hands-free control of water flow in kitchens bathrooms and gardens.
- Quick shutdown of water supply in case of emergencies.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Hands-free operation convenient enhances accessibility for those with mobility issues.
Cons: Requires compatible smart home assistant potential privacy concerns with always-listening devices relies on stable internet connection may have occasional misinterpretation of voice commands.
Basic Setup Instructions
- Make your valve’s controlling device is compatible with your preferred voice assistant.
- Set up the valve’s controller according to manufacturer instructions.
- Enable the corresponding skill or action in your voice assistant app.
- Link your device account to your voice assistant.
- Test voice commands to control your valve.
Advanced Valve Automation
These ideas are for those seeking a higher degree of customization and control over their valve automation. These options cater to tech-savvy individuals who enjoy tinkering and creating custom solutions for their homes. They require more technical knowledge but provide powerful capabilities for complex automation scenarios.
DIY Microcontroller Projects - Arduino or Raspberry Pi

Arduino and Raspberry Pi are popular microcontrollers used in DIY electronics projects. They offer a flexible and highly customizable platform for creating your own valve automation systems. These devices can be programmed to read sensors control valves and even provide a web interface for remote control.
Common and practical uses
- Custom irrigation systems with precise control
- Smart water leak detection and prevention systems
- Automated hydroponics setups
- Personalized home water management systems
Pros and cons
Pros: Highly customizable and expandable cost-effective for complex systems great learning opportunity for DIY enthusiasts interested in electronics and programming can integrate with a wide range of sensors and devices.
Cons: Requires programming skills and electronics knowledge may not be as reliable as commercial solutions without proper setup time-consuming to setup and troubleshoot.
Examples of Microcontrollers
- Arduino Uno
- Raspberry Pi 4
- ESP32 development board
Basic setup instructions
- Choose your microcontroller platform.
- Gather necessary components (relay modules sensors power supply etc.).
- Design your circuit and connect components.
- Program your microcontroller using the appropriate IDE.
- Test your system and iterate on the design as needed.
Sensor-Based Automation

Sensor-based automation uses various sensors to monitor environmental conditions and automatically control valves based on real-time data. Sensors can detect parameters such as moisture flow level temperature pressure motion and more.
Common Types of Sensors for Valve Automation:
- Moisture Sensors: Detects the moisture level in soil or other materials. Used for irrigation systems.
- Flow Sensors: Measure the flow rate of liquids or gasses in a system. Used to detect leaks and monitor water usage.
- Level Sensors: Measure the level of liquids in tanks or containers. Used for maintaining water levels in pools or aquariums.
- Temperature Sensors: Measure temperature. Useful for HVAC and other temperature-sensitive applications.
- Pressure Sensors: Detect pressure levels in pipelines and tanks. Used for safety systems that shut off valves in case of overpressure.
- Motion Sensors: Detects nearby motion. Trigger automations like automatic pet feeders security sprinklers or water feature activation.
Ways to integrate sensors into valve automation:
- Choose Appropriate Sensors: Select sensors based on the specific requirements of your application.
- Connect Sensors to Controller: Integrate sensors with your PLC microcontroller or smart home system.
- Program Automation Logic: Write code or configure the controller to react to sensor inputs.
- Test and Calibrate: Ensure the sensors are functioning correctly and adjust the system as needed.
Common and practical uses:
- Automated smart garden and lawn watering
- Water level management in tanks and pools
- Temperature regulation in heating and cooling systems
- Pressure control in industrial processes.
- Motion-activated water features or security systems
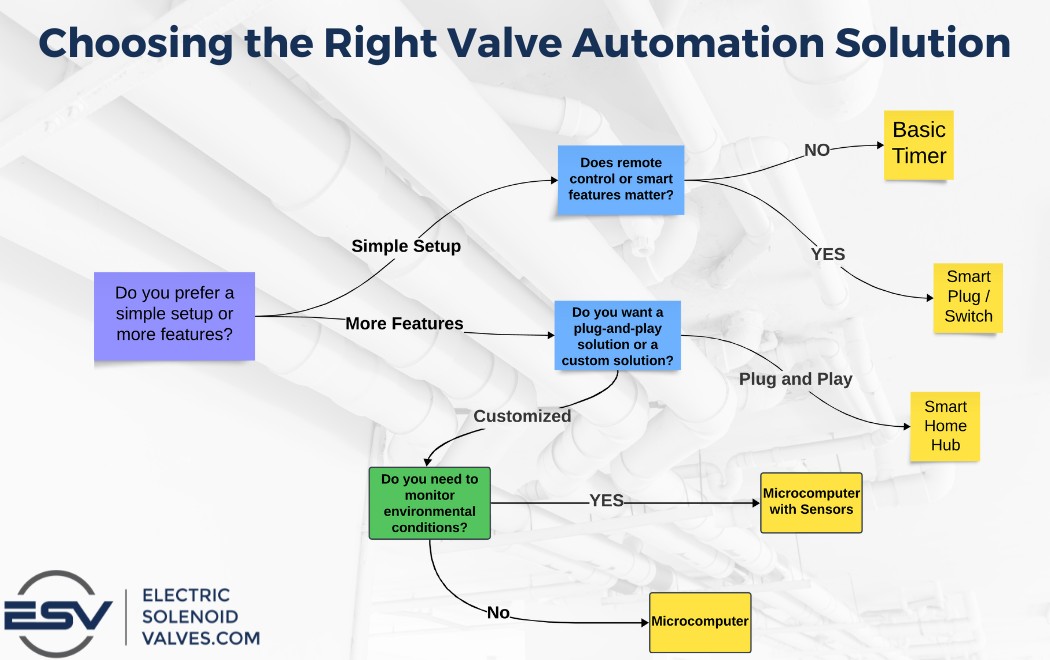
Choosing the Right Solution
As you can see there are plenty of options out there for remotely or automatically controlling your valves. It may feel overwhelming to figure out which automation option you should choose.
To simplify the decision-making process here is a simple decision path that should help in most scenarios:
DIY Valve Automation Projects at Home
Basic Setup: Automated Garden Watering
Control a simple drip irrigation system to water your plants as set times.
Materials Needed:
- Normally Closed Solenoid Valve: Choose one that's compatible with your water pressure and voltage. Use a valve with the correct thread size for your hose or pipe usually it’ll be a ¾” solenoid valve for the most popular sized hoses.
- Timer: A basic plug-in timer will work perfectly. Look for one that allows you to set multiple on/off cycles per day.
- Drip Irrigation System: This will ensure even water distribution to all your plants. You'll need tubing emitters (drip heads) and potentially a pressure regulator.
- Adapters (if needed): You might need adapters to connect different sized hoses or pipes.
Setup Instructions:
- Connect the Solenoid Valve: Attach the solenoid valve to your main water supply line. Use appropriate fittings and Teflon tape to get a watertight seal.
- Connect the Timer: Plug the timer into a standard electrical outlet then plug the power supply for the solenoid valve into the timer.
- Wire the Solenoid Valve: Connect the wires from the solenoid valve to the power supply following the manufacturer's instructions.
- Set Up the Drip Irrigation: Run drip irrigation tubing from the solenoid valve to your plants. Place emitters (drip heads) near the base of each plant.
- Program the Timer: Set the timer to turn on and off at desired intervals throughout the day. Start with shorter durations (e.g. 15-20 minutes) and adjust as needed based on your plants' watering requirements.
Advanced Setup: Fully Automated Greenhouse Control System
Design a comprehensive automation system for a greenhouse using microcontrollers and various sensors. You can create an automated greenhouse system that maintains ideal temperature humidity and light levels for your plants.
Materials Needed:
- Microcontroller: Arduino Mega or Raspberry Pi 4
- Temperature Sensors: DHT22 or DS18B20 (waterproof)
- Humidity Sensors: DHT22 or BME280
- Light Sensors: TSL2561 or BH1750
- Electric Ball Valves: For irrigation control choose size based on your water lines.
- Fans: 12V DC fans for air circulation
- Heaters: Small greenhouse heaters with thermostats
- Grow Lights: LED grow lights for supplemental lighting.
- Relay Modules: To control valves fans heaters and lights.
- Power Supply: 12V for valves and fans appropriate power for heaters and lights
- Enclosure: Waterproof box to house electronics
- Wiring: Various gauge wires for sensors and power connections
Setup Instructions:
- Install Sensors:
- Place temperature and humidity sensors at various heights in the greenhouse.
- Install light sensors near plant levels.
- Use waterproof housings for sensors if needed.
- Set Up Microcontroller:
- If using Arduino install it in the waterproof enclosure.
- For Raspberry Pi set up Raspberry Pi OS and install it in the enclosure.
- Connect Hardware:
- Wire sensors to appropriate pins on the microcontroller
- Connect relay modules to the microcontroller.
- Wire valves fans heaters and lights to the relay modules
- Program the System:
- Write code to read data from all sensors.
- Create control logic for maintaining optimal conditions.
- Implement a simple user interface for monitoring and manual control.
- Install Equipment:
- Mount fans for air circulation.
- Install heaters in appropriate locations.
- Set up grow lights above plant areas.
- Install electric ball valves in your irrigation system.
- Create Automation Rules:
- Set temperature thresholds for fan and heater activation.
- Program light schedules based on plant needs.
- Create humidity-based watering cycles.
- Test and Calibrate:
- Run the system and monitor plant health and growth.
- Adjust sensor thresholds and control parameters as needed.
- Fine-tune automation rules for optimal growing conditions.
Ready to take the next step?
Share your DIY valve automation projects with us on social media! We'd love to see how you're using this technology to enhance your home. Tag us on Instagram (@electricsolenoidvalves) with your creations. Check out some of the DIY valve automations from our customers.
Need help choosing the right solution? Contact us for advice and recommendations on choosing the right valves for your project. Our valve experts are here to help you find the perfect valve automation system for your needs.
Order now! Our warehouse has a full inventory of control valves ready to ship out today. Get your orders fast when you order from Electricsolenoidvalves.com.